Posted by Spycor Building on Mar 7th 2025
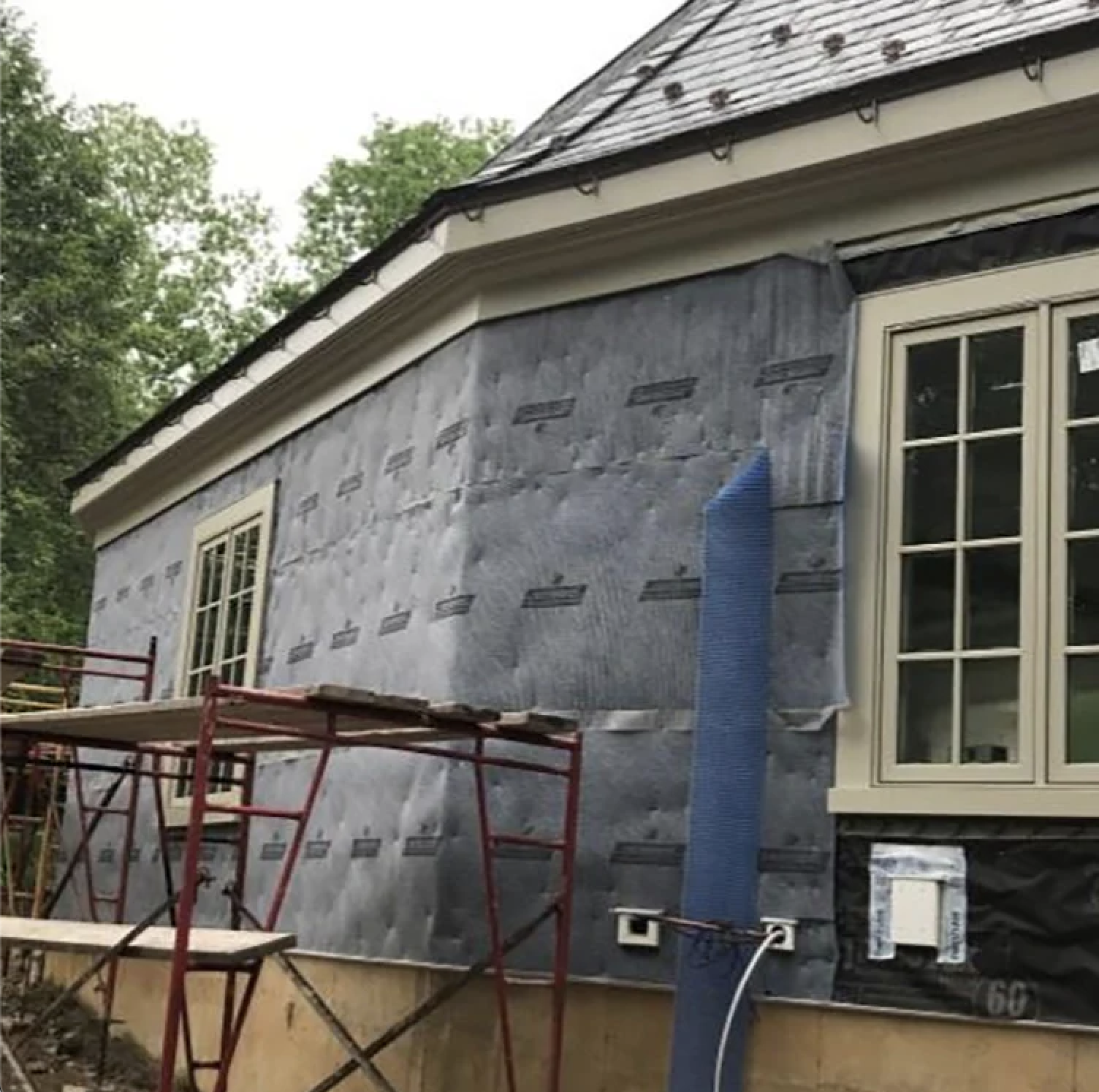

What is a Rainscreen and Why Does It Matter?
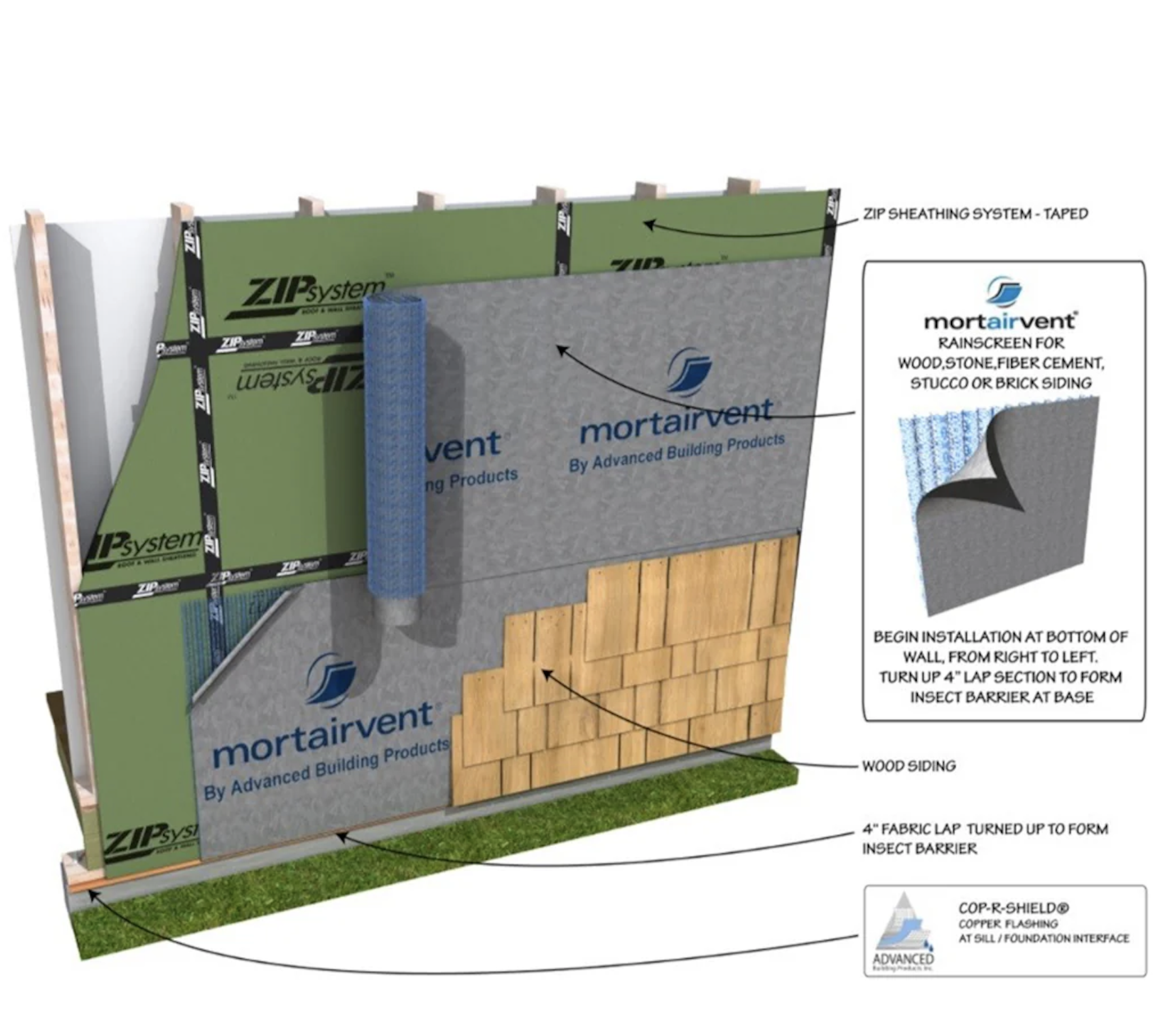
A rainscreen is an advanced exterior cladding system designed to protect buildings from moisture intrusion by creating a ventilated air gap between the siding and the underlying structure. This construction technique plays a vital role in modern building science, improving a structure’s durability, longevity, and energy efficiency.
By preventing trapped moisture, a well-designed rainscreen system helps mitigate mold growth, rot, and structural damage, all of which can lead to costly repairs over time. Rainscreens also contribute to a more energy-efficient building envelope, reducing heating and cooling costs by improving insulation and allowing walls to dry faster after exposure to rain or humidity.
Breaking Down the Rainscreen System
A rainscreen assembly consists of three key components that work together to form a highly effective moisture management system:
1. Water-Resistive Barrier (WRB)
The WRB is the first line of defense in preventing water from penetrating the building’s structural components. It is a continuous layer installed behind the exterior cladding, typically made from materials such as:
- Asphalt-saturated felt
- House wraps (e.g., Tyvek or other synthetic sheets)
- Liquid-applied membranes
- Self-adhered or mechanically fastened WRBs
The WRB blocks water from reaching wood, insulation, drywall, or framing, preventing moisture-related damage while allowing vapor permeability to let trapped moisture escape.
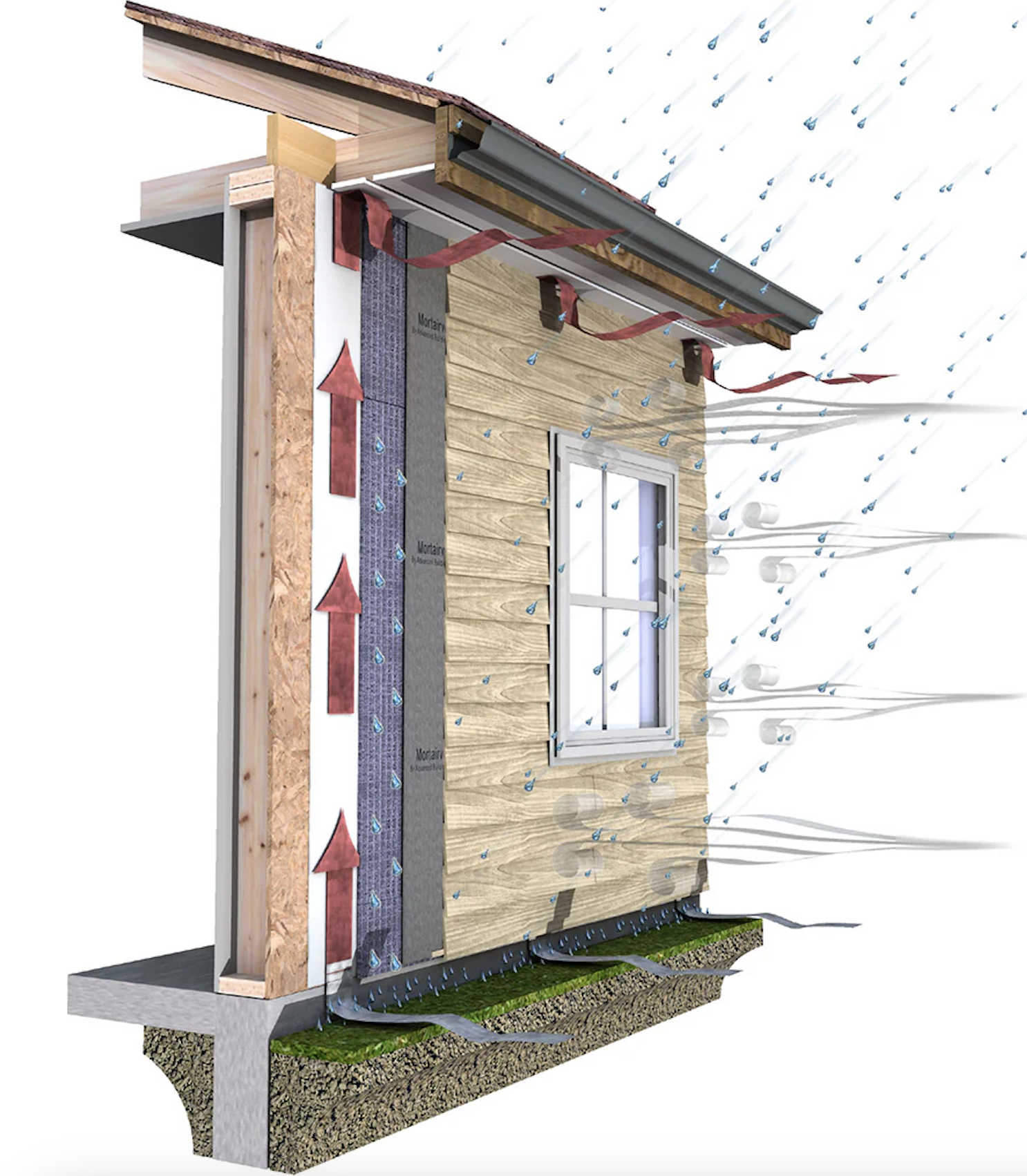
2. Air Gap (Drainage and Ventilation Cavity)
The air gap between the WRB and the cladding is a critical feature that differentiates rainscreens from traditional wall assemblies. This ventilated space serves two key functions:
- Drainage: Any water that gets past the cladding can safely flow downward and exit through weep holes at the base of the wall.
- Ventilation: The air gap promotes airflow behind the cladding, helping the wall system dry quickly and reducing the risk of trapped moisture.
The width of the air gap varies based on project requirements but is typically between 3/8 inch and 3/4 inch, with some high-performance systems using even larger cavities for enhanced drying potential.
3. Exterior Cladding (First Layer of Defense)
The cladding is the outermost protective layer that shields the building from direct exposure to wind, rain, UV rays, and other environmental factors. It also provides aesthetic appeal and can be made from a wide range of materials, including:
- Fiber cement
- Wood siding
- Brick veneer
- Metal panels
- Stone or composite materials
Although cladding is not 100% watertight, it plays a crucial role in reducing the amount of water that reaches the underlying layers. By working together with the WRB and air gap, the cladding ensures that any infiltrating moisture can drain and evaporate efficiently, preventing long-term structural damage.

Benefits of Rainscreen Systems
Implementing a rainscreen system provides multiple advantages, making it an essential feature in modern construction. These systems not only protect buildings from moisture damage but also contribute to their longevity, efficiency, and aesthetic appeal.
1. Superior Moisture Management
One of the primary functions of a rainscreen is moisture control. Unlike traditional wall assemblies, where water can become trapped behind the cladding, a rainscreen system creates a ventilated air gap that allows any water that penetrates the outer layer to:
✔ Drain downward through weep holes at the base of the wall.
✔ Evaporate as air circulates through the cavity.
This prevents moisture buildup, reducing the risk of mold growth, rot, and freeze-thaw damage, which can compromise the building’s structural integrity.
2. Enhanced Durability & Reduced Maintenance Costs
Moisture-related issues like wood decay, rust, and material deterioration can significantly shorten a building’s lifespan. A properly installed rainscreen system helps extend the life of building materials by keeping them dry and free from prolonged exposure to water.
Buildings with rainscreens require fewer repairs and lower long-term maintenance costs, as they experience less moisture damage, cracking, and material degradation over time.
3. Improved Energy Efficiency
A well-ventilated rainscreen system enhances a building's thermal performance, contributing to better insulation and lower energy costs. The air cavity acts as a buffer zone, reducing heat transfer and helping regulate indoor temperatures.
✔ In hot climates: The rainscreen prevents excessive solar heat gain, keeping buildings cooler and reducing air conditioning costs.
✔ In cold climates: It minimizes heat loss by reducing thermal bridging, improving energy retention inside the building.
This added insulation reduces reliance on heating and cooling systems, resulting in lower energy consumption and improved sustainability.
4. Aesthetic Flexibility & Design Versatility
One of the biggest advantages of rainscreen systems is their compatibility with various cladding materials, allowing architects and builders to achieve modern, stylish, and customizable exteriors without compromising performance.
✔ Suitable for fiber cement, wood, brick veneer, metal panels, natural stone, composite materials, and more.
✔ Allows for unique textures, colors, and architectural styles, accommodating both traditional and contemporary designs.
✔ Provides hidden fastening systems for a sleek, seamless appearance.
With a rainscreen, builders can prioritize both functionality and design, ensuring that buildings remain both visually appealing and structurally sound.
Types of Rainscreen Systems
Rainscreen systems are categorized based on how they manage water, air circulation, and pressure regulation. Selecting the right type depends on climate, building design, and specific project requirements.
1. Ventilated Rainscreens
Best for: Areas with high humidity and frequent rainfall.
✔ These rainscreens have openings at both the top and bottom of the cladding, allowing for continuous airflow and moisture evaporation.
✔ Promotes efficient drying and reduces the risk of mold, mildew, and water damage.
✔ Commonly used in residential and commercial projects where maximum ventilation is required.
2. Drained and Back-Ventilated Rainscreens
Best for: Moderate climates with occasional moisture exposure.
✔ These systems feature drainage openings at the bottom, allowing water to escape while maintaining limited ventilation.
✔ The design minimizes airflow while still preventing moisture buildup, making it a balanced option between ventilation and insulation.
✔ Frequently used in brick veneer and stucco applications, where controlled moisture management is necessary.
3. Pressure-Equalized Rainscreens (PERs)
Best for: Windy and extreme weather conditions.
✔ Designed to balance air pressure within the cavity, preventing wind-driven rain from being forced behind the cladding.
✔ Small ventilation compartments break up the air pressure, significantly reducing water infiltration.
✔ Common in high-rise buildings, coastal areas, and regions with severe weather exposure.
Best Practices for Rainscreen Installation
A properly installed rainscreen system plays a crucial role in protecting buildings from moisture damage, improving energy efficiency, and extending structural longevity. To ensure optimal performance, it’s essential to follow these best practices during installation.
1. Ensure Proper Air Gap Width
Why it matters: The air gap allows moisture to drain and evaporate, preventing water buildup behind the cladding.
✔ Maintain a minimum 3/8-inch gap, though 3/4 inch to 1 inch is ideal for enhanced ventilation.
✔ Ensure uniform spacing across the wall to prevent water stagnation or air blockage.
✔ Use furring strips or a dedicated rainscreen drainage mat to create a consistent gap.
A well-ventilated cavity ensures efficient drying and prevents trapped moisture, reducing the risk of mold, rot, and material degradation.
2. Use Durable, Moisture-Resistant Materials
Why it matters: Prolonged exposure to moisture can weaken building materials, leading to structural failure and costly repairs.
✔ Select rot-resistant furring strips such as pressure-treated wood, PVC battens, or metal furring channels to prevent decay.
✔ Choose high-performance exterior cladding materials, including fiber cement, metal panels, or composite siding, that resist moisture absorption.
✔ Utilize a high-quality Water-Resistive Barrier (WRB) to provide an extra layer of protection against water intrusion.
Investing in durable materials enhances the lifespan of the rainscreen system and minimizes long-term maintenance costs.
3. Incorporate Effective Flashing Systems
Why it matters: Improperly sealed openings around windows, doors, and penetrations are common entry points for water, leading to leaks and interior damage.
✔ Install continuous flashing around windows, doors, roof-wall intersections, and foundation joints to direct water away from vulnerable areas.
✔ Use self-adhering, waterproof flashing tapes for added moisture protection in critical areas.
✔ Ensure flashing is correctly layered with the WRB to prevent water from seeping behind it.
Proper flashing installation prevents leaks and enhances the overall effectiveness of the rainscreen system.
4. Install Insect and Debris Screens
Why it matters: Ventilation openings at the top and bottom of the rainscreen cavity improve airflow but can also become entry points for insects, rodents, and debris.
✔ Use stainless steel or corrosion-resistant insect screens to block pests while maintaining airflow.
✔ Ensure adequate opening size (⅛ inch or smaller) to keep out insects while allowing for ventilation.
✔ Periodically check and clean the screens to prevent blockages that could restrict airflow.
Screens protect the integrity of the ventilation system, ensuring unobstructed airflow and drainage.
5. Perform Regular Maintenance and Inspections
Why it matters: Even the best rainscreen system requires ongoing maintenance to function properly over time.
✔ Conduct annual inspections to check for clogged weep holes, dirt buildup, or damaged furring strips.
✔ Look for cracked, loose, or deteriorating cladding panels and replace them as needed.
✔ Ensure that flashing, WRB, and ventilation gaps remain intact and effective.
Routine maintenance extends the life of the rainscreen system, preventing costly water damage and repairs.
Incorporating a rainscreen system into your construction project is a proactive step toward moisture control, enhanced durability, and improved energy efficiency. By following best practices such as maintaining a proper air gap, using moisture-resistant materials, installing flashing correctly, preventing pest entry, and performing regular maintenance, you can ensure your rainscreen system delivers long-term protection and performance.
CLICK HERE to explore the best rainscreen solutions for your building project!


